The airline industry relies heavily on business intelligence (BI) and airline data analytics to streamline operations, improve efficiency, and enhance customer experiences. Business intelligence in the airline industry allows airlines to collect and analyze vast amounts of data, ranging from flight schedules to passenger preferences, enabling better decision-making and operational control. With the integration of artificial intelligence in the airline industry, airlines can further optimize their services, predict trends, and enhance their overall business strategies.
Key Benefits of BI in the Aviation Industry
The implementation of business intelligence in the aviation industry offers numerous advantages. By leveraging BI tools, airlines can optimize processes, reduce costs, and improve service delivery. Data analytics in the airline industry also plays a crucial role in driving innovation and addressing operational challenges. Airlines can use this data-driven approach to enhance fleet management, minimize delays, and provide passengers with a smoother travel experience.
The Main Applications of BI and Data Science in the Airline Industry
Business intelligence has various applications across airline operations, contributing to both efficiency and profitability. Below are the primary areas where BI in airline operations management can make a significant impact:
Revenue Management
BI tools help airlines analyze market demand, customer behavior, and pricing trends. This enables airlines to optimize ticket pricing and maximize revenue through dynamic pricing strategies. Airlines can adjust fares based on factors like seasonality and route popularity, ensuring profitability.
Crew Management
Crew scheduling is a complex aspect of airline operations. Business intelligence tools streamline crew management by analyzing staffing needs, tracking work hours, and ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements. These tools minimize scheduling conflicts and improve operational efficiency.
Operational Efficiency
Operational data analytics allow airlines to identify inefficiencies in their processes. BI in the airline industry helps improve ground operations, baggage handling, and aircraft turnaround times. By leveraging data insights, airlines can make their operations more cost-effective and time-efficient.
Flight Schedule Management to Reduce Cancellations
Business intelligence systems enable airlines to analyze historical data and weather patterns, helping to optimize flight schedules and reduce cancellations. By predicting disruptions, airlines can proactively adjust flight plans and minimize inconvenience for passengers.
Improve Operations & Customer Satisfaction
Business intelligence enhances customer satisfaction by analyzing passenger feedback, preferences, and travel patterns. Airlines can personalize services, improve onboard experiences, and offer loyalty programs based on this data, which helps boost customer loyalty and retention.
Some Airlines Using BI to Improve Operations
Several airlines have successfully adopted business intelligence in their operations to improve efficiency and deliver better services:
Delta Air Lines, Lufthansa, and American Airlines use BI and data analytics in the airline industry to enhance flight scheduling, minimize delays, and improve customer experiences. They employ advanced airline business intelligence systems to optimize operations, manage crew schedules, and enhance revenue management. Additionally, they leverage BI tools to improve operational decision-making and enhance customer service through real-time data analysis.
The use of business intelligence offers airlines several strategic advantages:
- Enhanced decision-making: BI tools provide real-time insights, enabling data-driven decisions.
- Operational efficiency: Streamlining processes leads to cost savings and improved performance.
- Customer experience: Tailored services and real-time adjustments enhance customer satisfaction.
- Cost reduction: BI helps airlines identify cost-saving opportunities in areas like fuel management, crew scheduling, and route optimization.
Conclusion
Business intelligence is transforming the airline industry by optimizing operations, enhancing revenue management, and improving customer satisfaction. Airlines that adopt a robust BI strategy are better positioned to operate efficiently and remain competitive. From reducing flight cancellations to improving crew management, the applications of business intelligence in aviation are vast and continue to evolve, ensuring better operational outcomes and superior passenger experience.
Mu Sigma’s decades of experience in data analytics can help airlines build seamless BI platforms to maximize revenues and improve customer experiences. We conduct a thorough assessment of your current landscape, develop a tailored plan, execute data migration and tool configuration, and provide comprehensive user training. With our expertise in cutting-edge data-driven solutions and end-to-end support, you can rest assured that your new BI platform is optimized for success.
]]>Business Intelligence (BI) refers to the technologies, processes, and tools used by organizations to collect, analyze, and present business data. The goal of business intelligence is to provide actionable insights that improve decision-making, operational efficiency, and strategic planning. A solid business intelligence strategy involves leveraging BI tools and platforms to extract value from vast amounts of data, ultimately driving better business performance.
What are the Benefits of Using BI?
The adoption of business intelligence tools offers numerous benefits to organizations, such as improving decision accuracy, enhancing productivity, and optimizing resource allocation. A well-defined business intelligence platform can streamline data collection, data integration, and analytics, offering a single source of truth for all business-related insights. By incorporating BI into business processes, companies can remain competitive, agile, and data-driven.
7 Ways Business Intelligence Can Transform Your Business Performance
1. Enhanced Decision-Making
Business intelligence tools provide organizations with real-time data and insights that support accurate and informed decisions. With a comprehensive view of business performance, leadership can make strategic choices faster and with greater confidence.
2. Operational Efficiency
BI tools help organizations identify bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and waste in their operations. By analyzing performance data, businesses can streamline processes, optimize resource utilization, and reduce costs.
3. Improved Customer Insights
BI enables businesses to analyze customer behavior and preferences, allowing them to tailor products, services, and marketing efforts. This leads to enhanced customer satisfaction and loyalty while driving business growth.
4. Performance Monitoring
Business intelligence platforms allow for the continuous monitoring of key performance indicators (KPIs) across various departments. Businesses can track their progress in real-time and make adjustments as needed to achieve goals more effectively.
5. Increased Agility
A strong business intelligence strategy gives organizations the agility to respond to market changes swiftly. By analyzing trends and identifying potential risks early, companies can pivot their strategies and stay ahead of the competition.
6. Data-Driven Innovation
BI tools foster innovation by highlighting trends and patterns that may not be immediately apparent. By identifying opportunities for new products, services, or process improvements, organizations can innovate faster and more effectively.
7. Revenue Growth
BI tools help businesses identify profitable opportunities and cost-saving measures. From optimizing pricing strategies to refining sales techniques, business intelligence drives revenue growth by enabling better financial planning and execution.
Incorporating business intelligence into daily operations offers organizations a competitive edge. With the right BI strategy in place, businesses can leverage data to make smarter decisions, drive growth, and improve performance.
With Mu Sigma’s extensive expertise in data analytics, airlines can unlock the full potential of business intelligence (BI) to drive performance. Our approach begins with assessing your data landscape, crafting a customized BI strategy, and implementing a seamless migration and tool configuration process. By leveraging data-driven insights, companies gain a clearer view of revenue opportunities, operational efficiencies, and customer needs. From initial setup to comprehensive user training, Mu Sigma’s end-to-end support ensures that your BI platform not only enhances current performance but also fosters agility and innovation, keeping your business ahead in a competitive market.
]]>Business Intelligence (BI) refers to the process of collecting, analyzing, and interpreting business data to make informed decisions. BI tools and business intelligence platforms enable businesses to access data from various sources, perform data analysis, and extract actionable insights. These insights support decision-making, allowing businesses to enhance efficiency and achieve strategic goals. The business intelligence process involves several steps, including data collection, integration, analysis, and reporting.
Business Intelligence in Business
In the current data-driven environment, BI has become a crucial aspect of business operations. Business intelligence systems support data analysis and business intelligence efforts, enabling companies to gather insights that drive competitive advantage. By using BI tools and techniques, businesses can transform raw data into meaningful business intelligence insights that improve decision-making processes.
Why Business Intelligence Is Important
Business intelligence plays a pivotal role in ensuring businesses operate more effectively. BI and analytics help businesses anticipate trends, improve operational efficiency, and make better strategic decisions. Business intelligence solutions enable organizations to monitor key performance indicators (KPIs) and evaluate progress toward goals. BI intelligence helps optimize processes, improve customer service, and identify areas for cost reduction.
Types of Business Intelligence Tools and Applications
Organizations use several types of business intelligence tools and applications to extract, process, and visualize data. These include:
- BI tools for data visualization: Tools such as Power BI and Tableau present data visually.
- Business intelligence software: Software platforms that support BI and analytics, providing data access, integration, and visualization capabilities.
- Top business intelligence software: These platforms include robust data analytics and reporting features.
- BI business intelligence solutions: Tools that offer solutions tailored to business-specific needs.
Key Areas Business Intelligence Improves the Way Work
Business intelligence enhances several areas of operations, including:
- Data-driven decision-making: BI tools allow organizations to base decisions on data, improving accuracy and outcomes.
- Operational efficiency: Business intelligence solutions streamline workflows and eliminate inefficiencies.
- Customer insights: BI techniques analyze customer behavior, helping organizations refine their offerings.
Types of BI Users and Benefits of BI
A variety of roles use BI systems within an organization. BI data analysts, managers, and executives all use business intelligence tools and techniques to support their work. The benefits of BI are widespread, helping businesses improve data-driven decision-making, enhance efficiency, and reduce costs.
With decades of experience in data analytics, Mu Sigma empowers businesses to create seamless business intelligence (BI) platforms. Leveraging cutting-edge BI tools and comprehensive support, Mu Sigma ensures that your BI platform is not only optimized for current needs but also adaptable for future insights, driving informed decisions that improve operational efficiency and customer engagement.
How Are BI Systems Implemented?
Business intelligence systems are implemented through a structured process that involves data collection, processing, and integration. BI tools for data visualization and reporting help present insights to key stakeholders. Implementation often starts with selecting the right business intelligence software that suits organizational needs. Integration with existing data sources is critical for ensuring the system operates efficiently. Continuous monitoring and adjustment ensure the system evolves with business needs.
Categories of BI Analysis
There are several categories of BI analysis, including:
- Descriptive analytics: Provides insights into past performance.
- Inquisitive analytics: Answer the question: Why did something happen at a certain moment in the past?
- Predictive analytics: Forecasts future outcomes based on historical data.
- Prescriptive analytics: Recommends actions based on analysis.
Business Intelligence Solutions
Business intelligence tools and techniques enable organizations to gather and analyze data from multiple sources. These solutions allow businesses to generate reports, visualize data, and make more informed decisions. Business intelligence tools and software are crucial for operational efficiency, cost control, and strategic planning.
BI Platforms
Top business intelligence software platforms include features such as real-time data access, integration with various data sources, and advanced data analytics. These platforms enable businesses to extract insights from large data sets, making them invaluable for data-driven decision-making.
BI vs. Data Analytics
Although business intelligence and data analytics are often used interchangeably, they refer to different processes. BI focuses on providing insights from historical data, while data analytics encompasses a broader set of practices, including predictive and prescriptive analytics. BI tools for data visualization are primarily used to present findings from descriptive analytics.
Examples of BI Systems Used in Practice
Business intelligence systems are used across industries to support decision-making. For instance, retailers use BI platforms to track sales patterns and optimize inventory. Manufacturers rely on BI to enhance operational efficiency and reduce costs. A visual representation of a typical BI system may include a data warehouse, a BI tool for data visualization, and a reporting interface for decision-makers.
Real-Life BI Examples
A leading retail chain partnered with Mu Sigma to improve its inventory management process using business intelligence insights. By leveraging BI tools and data analytics, the company optimized its stock levels and reduced inventory costs. Mu Sigma’s BI solutions allowed the retailer to monitor sales data in real-time, enabling faster and more accurate decision-making.
Also Explore: The Art of Problem Solving System
Summary
Business intelligence has become a critical component of modern business operations. BI tools, platforms, and solutions allow organizations to gather data, perform analysis, and generate insights that drive decision-making. Business intelligence and analytics support businesses in improving operational efficiency, reducing costs, and enhancing strategic decision-making. Whether it’s descriptive analytics or predictive forecasting, BI plays a central role in the way businesses operate and compete in today’s market.
]]>I recently purchased a new laptop and expected to receive recommendations for relevant accessories or complementary products. Instead, I was bombarded with ads for the same model I just bought, leaving me feeling like my recent purchase had gone unnoticed.
This begs the question: Why do retailers, from industry giants with substantial resources to smaller players, struggle to achieve genuine customer-centricity?
But are these conclusions based on isolated experiences, lacking any substantial evidence? Not at all.
During our engagement with a leading retailer’s e-commerce division, we discovered that 80% of product recommendations were repetitive, indicating an opportunity to enhance the personalization strategy.
It’s a paradox that plagues the industry. With rising consumer expectations and shrinking attention spans, retailers find it challenging to use data effectively to drive loyalty and growth. The root cause lies in the siloed nature of customer data, making it difficult to create a unified view of the customer’s journey and translate data into meaningful actions.
Most retailers capture vast data from touchpoints like facial recognition, heat maps, and purchase histories. The reality is that while market leaders are at the forefront of data-driven decision-making, many of their competitors are still relying on rudimentary tools that prioritize basic analytics over predictive insights. These tools often lack the sophistication to harness complex customer data for forecasting, real-time decision-making, and advanced personalization.
It’s like attempting to prepare an intricate dish without a recipe for a guest you’ve never met, guessing at ingredients and portions while navigating possible dietary restrictions and allergies. Likewise, each data point is a piece of the customer journey. And without a comprehensive view, retailers struggle to create targeted campaigns and personalized experiences, ultimately alienating their customers, and squandering the potential of their data.
But why is it so challenging for companies to adopt a contextual customer experience (CX) approach?
Three key sticking points emerge:
-
Organizational Silos:
Departments often operate in silos with their own functional projects and priorities, leading to fragmented data and disjointed initiatives, hindering a unified customer view.
-
Legacy Infrastructure:
Outdated systems and data storage methods make it difficult to integrate and analyze data from multiple sources effectively.
-
Skill Gaps and Cultural Resistance:
Many organizations lack the necessary data literacy and analytical skills, or face resistance from employees accustomed to traditional methods.
To overcome these challenges and truly resonate with customers, retailers must holistically advance their data capabilities. This involves integrating existing data sources with real-time data capture across touchpoints to build a comprehensive customer view and unlock intelligent insights.
However, success hinges on operationalizing insights through dynamic decision engines that enable real-time personalization and contextual engagement, coupled with continuous testing to iteratively refine individualized experiences that delight consumers across all journeys.
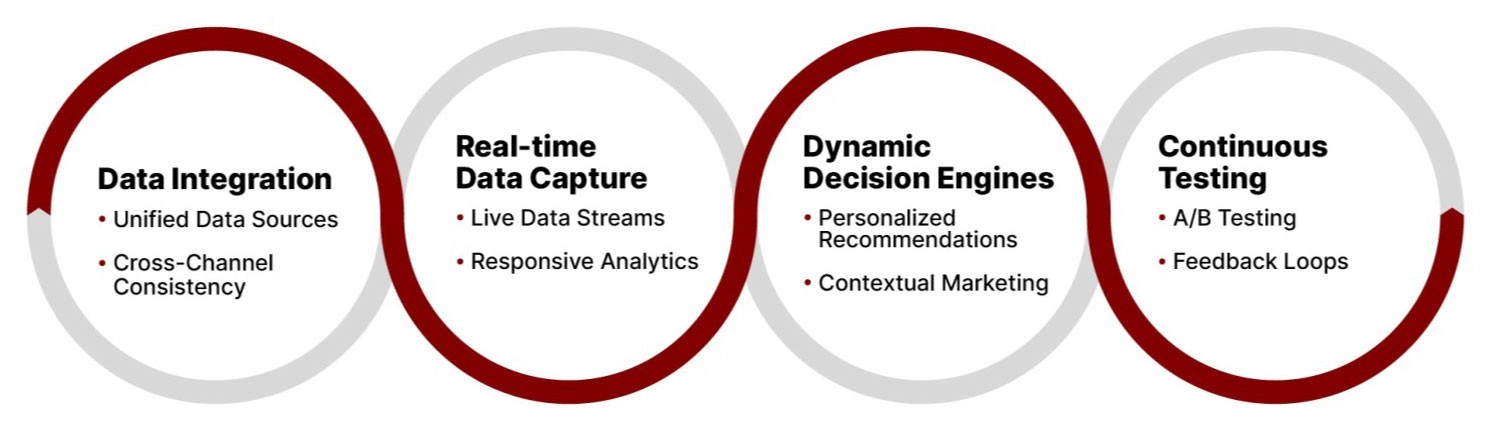
The era of personalized experiences and seamless shopping journeys isn’t on the horizon – it’s a reality that forward-thinking retailers are already embracing.
Sephora, for example, employs advanced tech like spectroscopic imaging and machine learning to provide personalized product recommendations tailored to individual complexions, showcasing strides in customer-centricity.
However, as retailers attempt to push the boundaries of personalization and contextualized experiences, the potential sacrifice of privacy for convenience becomes a pressing concern.
As retailers personalize experiences using customer data, they must balance personalization with preserving trust by prioritizing privacy. Building strong, lasting customer relationships requires innovative, holistic service that upholds ethical standards. True customer-centricity means cohesively integrating data and innovation into an authentic narrative.
Learn how Mu Sigma helps retailers worldwide navigate this complex landscape and unlock true customer-centricity. For more details, write to us at [email protected]
About the author
Chetan Jain is an analytics leader driving revenue growth, supply chain optimization, and data-driven decision-making across Fortune 500 CPG and retail organizations.
]]>Let’s examine it a little closely. Below is a statement and two questions with options. Pick the option you think is the most probable answer. Try to answer as quickly as possible and without any external assistance.
“Out of a group of 10 individuals, five have received their graduate degree from an Ivy League university, and five have dropped out. All 10 individuals have started businesses.”
Question 1:
Given that all individuals have studied in Ivy League colleges, how many individuals’ businesses will likely survive for more than five years?
- More than five
- Less than five
- Five
Question 2:
Given that Ivy League dropouts, including Bill Gates and Mark Zuckerberg, have started successful businesses, how many college dropouts’ businesses will likely survive for more than five years, compared to those who have received their degrees?
-
- The numbers are equal
- More college dropouts’ businesses will likely survive for more than five years than those with a college degree
- Fewer college dropouts’ businesses will likely survive for more than five years than those with a college degree
unnamed 1 2
If you chose option 3 for both questions, you are probably closest to the right answer. The U.S. Small Business Association pegs the likelihood of a new business surviving for more than five years at about 50%. Similarly, a Harvard Business Review study showed that only about 4% of college dropouts had started successful businesses, compared to more than 60% of graduates.
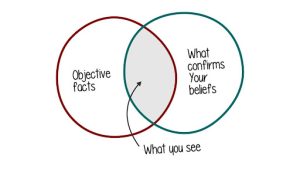
But don’t beat yourself up if you picked the wrong option. Most people are in the same boat as you because most people come with inherent biases. The bias that may have affected you in this case was the ‘anchoring bias.’
Anchoring bias occurs when individuals rely too heavily on the first piece of information encountered, using it as a reference point for subsequent judgments. In the instances above, the first piece of information you got in Question 1 was that all are Ivy League students, and you may have immediately anchored that information to companies and brands founded by such individuals, including Google and Facebook. Similarly, in Question 2, your anchor was the fact that dropouts such as Gates and Zuckerberg have founded successful companies, which may have led you to believe that many Ivy League dropouts are successful entrepreneurs.
In data analysis, the anchoring bias can lead to an overreliance on initial data points or statistics, even if they are not representative of the overall dataset. For example, a financial analyst evaluating a company’s stock performance might anchor their analysis on the stock’s price at the beginning of the year, failing to account for subsequent fluctuations or market trends. Addressing anchoring bias requires you to consider a wide range of data points and avoid fixating on any single piece of information.
Biases Affect Decisions
In modern business, data-driven decision-making is key to strategic planning and operational efficiency. Organizations invest heavily in data collection, analysis, and development of advanced algorithms to gain a competitive edge. However, cognitive biases inherent in human thinking can compromise these efforts by distorting our interpretation of data and leading to suboptimal outcomes.
One common bias is confirmation bias, the inclination to seek and favor information that confirms preexisting beliefs. In data analysis, this means selectively focusing on data points that align with preconceived notions while downplaying or disregarding contradictory evidence. For instance, when evaluating a marketing campaign, a company might prioritize data indicating increased website traffic or social media engagement while overlooking data suggesting a decline in customer satisfaction.
The availability heuristic is another cognitive bias that can impact decision-making. This bias refers to the tendency to overestimate the likelihood of events based on their ease of recall. In data analysis, this can result in overemphasizing recent or salient events and neglecting less memorable but potentially more relevant data.
Finally, survivorship bias occurs when we focus exclusively on successful outcomes and ignore failures, leading to a distorted perception of reality. In data analysis, this manifests as analyzing only the data of successful projects, products, or individuals while neglecting data on failures. For example, a study examining the factors contributing to business success might focus solely on companies that have achieved growth or profitability while overlooking failed ventures.
To ensure effective data-driven decision-making, it is imperative to be aware of these cognitive biases and take steps to mitigate their impact. This can involve actively seeking out disconfirming evidence, systematically collecting and analyzing data over extended periods, and including data on both successes and failures in any analysis. By doing so, organizations can make more informed decisions based on a comprehensive understanding of the available data.
Mitigating Cognitive Bias for Better Decisions
While cognitive biases are inherent in human thinking, their influence on data-driven decision-making can be mitigated through various strategies. Gaining awareness of these biases among decision-makers and data analysts is the first step. Education and training programs can equip individuals with the knowledge and skills necessary to identify and address biases in their work.
The second step is establishing clear decision criteria before analyzing data, which can help ensure that decisions are based on objective evidence rather than subjective interpretations. Creating clear decision criteria involves defining specific metrics, thresholds, and success criteria that will guide the decision-making process.
Furthermore, fostering a culture of collaboration can be instrumental in mitigating cognitive biases. By involving individuals with diverse backgrounds, experiences, and perspectives in the decision-making process, organizations can gain a more comprehensive understanding of the data and reduce the likelihood of groupthink. Encouraging open discussion and debate, and actively seeking out dissenting opinions can also help expose and challenge biases.
Another key step is analyzing the data and forming hypotheses that can be confirmed and disproved using the available data. By actively employing a methodological approach to hypothesis testing in two scenarios of confirming and disproving the set hypothesis, one can challenge assumptions and reduce confirmation bias. Following this process encourages a comprehensive exploration of data, including metrics that contradict initial beliefs, potentially revealing hidden patterns or unexpected relationships. A rigorous approach fosters a more objective understanding of the data, leading to more robust insights and data-driven decisions grounded in reality rather than clouded by preconceived notions.
Finally, external validation can play a crucial role in ensuring the objectivity and reliability of data-driven decisions. Validation can involve peer review of findings, engaging external consultants, or utilizing independent data verification services.
Cognitive biases pose a significant challenge to effective data-driven decision-making. By understanding and actively addressing these biases, organizations can harness the power of data to make more informed, objective, and ultimately successful choices. Commit to ongoing learning, foster a culture of collaboration and diversity, and be willing to challenge assumptions and seek out unconfirming evidence. By embracing these principles, businesses can unlock the full potential of data-driven decision-making and achieve their strategic objectives.
About the Authors:
Richa Gupta, Business Unit Head at Mu Sigma, and Todd Wandtke Head of Marketing and Customer Success at Mu Sigma.
]]>Let’s say you’re a cheeky entrepreneur; what would you have done? Let’s look at two scenarios.
The first scenario is that you draw the liquid out by the barrel load and sell it as something that can be used as an alternative to firewood. It is the most obvious answer.
However, in the second scenario, you still have more questions on whether the liquid can be used for something greater than just household fuel. You want to explore other ways you can use the black liquid that could perhaps change the world for the better.
So, you find ways to refine the liquid into better products that can be used for different purposes. One of them could be refining it to replace animal fat in oil lamps, which would revolutionize household lighting in pre-electricity days. Another more advanced use is to refine it further so it can replace coal to power engines as a more efficient and safer fuel. You find ways to create fibers that can be used to replace traditional cotton or linen in textile manufacturing. You even find a way to derive a highly malleable material – plastic — that can be used in anything from aircraft interiors to food storage containers or the buttons on your shirt.
The point of this short illustration was to make a simple statement: discovering oil means nothing unless you explore, experiment and learn how to engineer it in better, more efficient ways.
The same is true for data.
The amount of data captured daily is staggering, with estimates reaching zettabytes (one zettabyte equals a trillion gigabytes). Businesses are collecting vast amounts of it from users through various channels, and there is an abundance of it. They are clamoring to collect more and more of it to derive insights about their customers so they can produce better products and services for them.
Data, however, is a mixed bag. Valuable insights reside alongside irrelevant or even misleading information. The core problem lies in the very nature of data. It can be messy and biased. “Crappy data in, crappy insights out” becomes a critical truth.
Just as transforming oil into usable products requires significant engineering, data demands a similar approach. Businesses that are dealing with data in such vast quantities today need a multi-disciplinary team with expertise in statistics, mathematics, business acumen, and data science. The team must continuously refine its capabilities to ensure clean and unbiased data.

The rise of Large Language Models (LLMs) might seem to diminish the role of data engineers. However, LLMs are only as effective as the data they’re trained on. In this sense, data today resembles plastic, a potential resource that can become a pollutant if not managed effectively. Biased data leads to biased AI outputs, which can have a domino effect, as biased data used in one system can propagate through interconnected systems. The real value lies not in collecting data but in the engineering expertise that transforms it into a powerful asset. In short, organizations must avoid becoming “data junkyards” – those who collect without the capability to translate it into value.
In the age of information overload, a critical shift in perspective is needed. The true goal is not collecting the data but empowering individuals and organizations to make better, faster, and more impactful decisions using data.
So, how can businesses transform their data to fuel their decisions?
Analytical rigor remains paramount. While advancements like prompt engineering, knowledge graphs, and question networks are valuable tools, the ability to ask the right question remains a human strength. It’s a skill honed over time and a mark of true intelligence.
Just like an oil baron in the 19th century found ways to refine crude oil further and further to make it more efficient, data engineers of the 21st century must find ways to make their data more efficient. Great engineers find ways to reduce the cost and the time of refining data into a meaningful and compelling product that can drive decisions.
The key question two hundred years ago was: “How can we build a more efficient refinery?” Recognizing the refinery was the key to unlocking value. In the same light, today’s key question is, “How do I build a better data exploration ecosystem?”
By effectively engineering data, the cost per question, both in terms of time and resources, will decrease. As such, the organization’s ability to answer more questions translates to greater preparedness for uncertainty. In this environment, optionality becomes the key to success, and generating options demands a constant flow of questions. It boils down to how clear the business is with its goals and objectives. Clarity is crucial for asking the right questions. Without it, organizations can linger.
The true potential of oil wasn’t realized until it was refined and utilized in new ways. The true value of data lies in its ability to inform better decision-making. By embracing a culture of curiosity and employing the right tools to unlock its potential, organizations can transform data from a raw resource into the fuel that propels them toward a future of innovation and success. The future belongs to those who can not only collect data but leverage its power to ask the right questions and make the best choices.
About the Authors:
Manaswitha Rao is a Business Unit Head who partners with clients in the retail and energy sectors. Todd Wandtke is the Head of Marketing and Customer Success.
]]>As Hurricane Season 2024 looms over coastal communities, insurers face a pivotal moment: customer relationships are no longer just about cutting checks. It’s about cutting through chaos. The companies that master proactive engagement during critical moments aren’t just processing claims 30% faster—they’re building deeper, lasting relationships. And in a world of rapidly evolving customer expectations, that’s the real victory.
Yet here’s the twist: while 40% of homeowners rush to increase coverage after disaster strikes, this urgency fades with time, leaving them vulnerable once again. So, how can insurers break this cycle of panic and complacency? The answer lies in data-driven innovation, which helps insurers keep pace with rapidly evolving customer needs long after the storm has passed.

Elevating the Customer Experience
Have you ever had to explain your issue to four different customer reps? 40% of policyholders have switched providers because of poor communication. For insurance customer experience executives, this is a wake-up call. Creating an omnichannel experience, from chatbots to in-person support, empowers customers to engage on their terms. And when disaster strikes, rapid claims processing and responsive service aren’t just important—they’re key moments that define their trust in you.
Proactive engagement doesn’t just address immediate concerns; it anticipates them. Insurers need to educate customers about their risks, maintain high levels of engagement, and prevent underinsurance in the long run. As such, user-friendly digital platforms become essential. Intuitive mobile apps, responsive websites and relevant content are no longer a luxury—they are the baseline for customer satisfaction in today’s on-demand economy.
Innovating Claims Management
Emerging technologies like AI, computer vision, and blockchain are revolutionizing claims processing, and insurance companies need to stay ahead of the curve. From automated document verification to predictive analytics, these tools streamline turnaround times and reduce fraud adding agility and efficiency to your operations.
Tailoring Coverage to Individual Needs
In an era where 70% of consumers are willing to share personal data (health, exercise, and driving habits) in exchange for lower insurance premiums, one-size-fits-all insurance is a relic of the past. Customers want policies tailored to their specific needs. The opportunity? Customizable plans with flexible limits and deductibles aligned precisely to each policyholder’s risk profile.
Usage-based models that leverage telematics data offer truly personalized premiums, helping insurers price policies more accurately and incentivize risk-reducing behaviors leading to more satisfied customers.
Fostering Proactive Engagement
Educating customers about disaster preparedness isn’t just a nice-to-have—it’s a must-do. Insurance providers who actively help policyholders mitigate risk, reduce losses and strengthen relationships. Beyond that, community involvement through partnerships with relief organizations shows that insurers genuinely care about the well-being of their policyholders.
A proactive approach is especially critical in regions facing market instability due to natural disasters. As larger insurers exit high-risk markets, smaller players may step in with unsustainable premiums. Established insurers, can maintain loyalty by engaging customers directly and offering solutions that weather even the fiercest storms.
Harnessing Data for Prescient Risk Assessment
Advanced data analytics allow insurers not just to react but also predict. By analyzing historical claims data, weather trends, and emerging risk factors, you can model the impact of climate change with increasing precision. Advanced Analytics enables you to adjust coverage options, pricing models, and risk management strategies proactively—putting you ahead of the curve.
Geospatial data adds an extra layer of insight, allowing insurers to develop highly localized risk profiles. From topography to flood zones, this granular understanding enables more accurate coverage, enhancing both customer trust and profitability.
At the same time, insurers need to address the low uptake of flood insurance in high-risk areas. By leveraging data to pinpoint protection gaps, you can innovate new products and outreach programs that ensure your customers are fully covered—before the next disaster hits.

Transforming Crisis into Opportunity
In 2023, global economic losses from natural disasters reached nearly $380 billion, largely due to severe earthquakes and storms. These staggering numbers highlight the growing financial impact of such events on economies worldwide. The companies that thrive in this new era won’t just be reacting to the next crisis – they’ll be anticipating it.
Whether it’s shifting markets or glaciers, some things are out of our hands—but your insurance strategy doesn’t have to be one of them. The question isn’t whether to transform – it’s how fast you can get there. Future-proof your operations while delivering a policyholder experience that stands the test of time.
Ready to write the next chapter in insurance innovation? Connect with our transformation experts today: Mu Sigma LinkedIn
]]>Business Intelligence (BI) refers to the combination of technologies, tools, and processes that organizations use to collect, analyze, and present data. The primary goal of business intelligence is to provide actionable insights that inform and improve decision-making. By leveraging business intelligence platforms and tools, organizations can access real-time data, analyze it, and make informed decisions that align with their strategic goals.
Adoption of BI in Businesses
The adoption of business intelligence has grown significantly in recent years. As organizations face increasing data volumes, BI has become essential for gaining a competitive edge. Companies are now investing in business intelligence applications and technologies that allow them to analyze data from multiple sources, monitor performance, and make data-driven decisions that improve efficiency and outcomes.
Importance of BI Tools for Effective Decision-Making
Business intelligence tools are critical for effective decision-making because they provide businesses with the ability to analyze data from various angles. By using tools like dashboards, data visualization, and reporting, organizations can identify trends, track key performance indicators (KPIs), and measure outcomes in real-time. These tools help companies avoid guesswork and ensure decisions are based on facts, not assumptions.
Business Intelligence Different from Other Analytics Tools
While other analytics tools focus primarily on data analysis, business intelligence technologies go beyond that by offering a comprehensive view of business operations. BI integrates data from different departments, enabling cross-functional analysis. It also offers advanced reporting capabilities that allow users to drill down into the data, providing a deeper understanding of business performance. In contrast, traditional analytics tools may only focus on specific datasets without offering the same level of integration and insight.
Mu Sigma helps organizations harness the power of business intelligence (BI) to drive informed decision-making, enhance operational efficiency, and achieve strategic objectives. From seamless data integration and tool configuration to user training, Mu Sigma ensures that your BI platform is optimized for current and future needs. With our support, your organization can transform raw data into actionable insights that improve performance, foster innovation, and strengthen competitive advantage in today’s data-driven marketplace.
Benefits of BI in Decision-Making
Several key benefits of business intelligence directly impact decision-making:
-
Improved accuracy:
By using real-time data, BI ensures that decisions are based on the most current and accurate information available.
-
Enhanced speed:
Business intelligence platforms enable faster data processing, reducing the time it takes to make critical decisions.
-
Better alignment:
BI tools ensure that decisions are aligned with the organization’s overall strategic objectives, improving the likelihood of achieving desired outcomes.
-
Risk management:
BI technologies help identify potential risks early, enabling businesses to take proactive measures before issues escalate.
Latest Trends in the Analytics Industry
The business intelligence industry continues to evolve with several emerging trends:
AI and Machine Learning Integration:
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are increasingly being integrated with business intelligence tools, allowing for predictive analytics and advanced data processing.
Self-Service BI:
Many companies are adopting self-service BI platforms, enabling employees to analyze data independently without relying on IT departments.
Cloud-Based BI Solutions:
Cloud-based business intelligence platforms offer scalability and flexibility, allowing organizations to access data anytime, anywhere.
Mobile BI:
The use of mobile applications for BI is growing, enabling decision-makers to access key insights on the go.
Summary
Business intelligence plays a pivotal role in improving decision-making by providing accurate, real-time data that supports informed and strategic decisions. Business intelligence tools and platforms allow companies to analyze data from multiple sources, offering insights that are critical for operational success. As the BI industry continues to evolve, organizations that adopt these technologies will be better equipped to make faster, more accurate decisions that drive business performance.
]]>Financial Fraud in the Digital Age
The days when fraud detection meant looking for suspicious IP addresses and unusual transactions are quaint now. Today’s fraudsters are deploying deep fakes for voice authentication bypass, using AI to mimic customer behavior patterns, and launching sophisticated attacks that adapt in real-time. The game has fundamentally changed, and traditional defenses are proving inadequate against this new wave of intelligent threats.
AI as the New Guardian of Financial Security
Banks are finally pulling ahead in this digital arms race. Traditional systems typically flag about 3% of suspicious activities, but AI-powered systems are catching seven times more potential threats. More impressively, false positives have plummeted from 60% to 22% in leading banks. Modern AI systems are processing over 100,000 transactions per second, analyzing more than 3,000 behavior variables simultaneously, and making decisions in under 300 milliseconds. Real-time intelligence has transformed the security landscape, enabling banks to detect and prevent 89% of fraud attempts even before the money moves. It’s not just an improvement – it’s a paradigm shift in defense capabilities against the financially crippling and reputational damaging frauds.
While a single unusual transaction might not signal fraud, banks must employ a risk-based approach to identify and mitigate potential threats. By assigning risk scores to suspicious activities, banks prioritize investigations and minimize the risk of fraudulent transactions. AI-enabled systems excel at identifying unusual and sophisticated customer behavior patterns, from analyzing purchase histories to tracking location data and account access timing. Most importantly, they can detect anomalies before they escalate into major security breaches.
Turbocharge Financial Services Visibility with AI
As AI rightfully garners significant attention, it’s crucial to recognize the often-overlooked areas that can bolster fraud prevention efforts. One such area is enhanced visibility and control over data. By illuminating potential vulnerabilities, organizations can proactively thwart cyberattacks. AI is revolutionizing how financial institutions handle their fragmented data and organizational structures, transforming traditional barriers into opportunities for enhanced fraud detection.
-
Breaking Down Data Silos:
AI systems can unify and analyze data across previously isolated systems. Advanced AI algorithms can simultaneously process information from multiple sources, such as transaction records, customer service interactions, online banking activities, and credit card usage patterns. Through sophisticated data integration techniques, AI can automatically standardize and correlate information from different formats and systems, creating a cohesive view of customer behavior.
For instance, AI might detect that while a customer’s credit card transactions appear normal in isolation, their combined pattern with recent changes in login locations and unusual wire transfer requests could signal potential fraud. A holistic analysis would be nearly impossible without AI’s ability to process and connect vast amounts of disparate data in real time.
-
Enabling Cross-Institutional Collaboration:
Many financial institutions operate with multiple lines of business, each with its teams and tools for fraud detection. While consolidating data is a crucial step, providing a holistic view of the entire organization empowers teams to collaborate effectively and identify broader patterns of fraudulent activity.
AI serves as a powerful enabler of collaboration across different departments and business lines. Modern AI platforms can create standardized risk assessments and alerts that are meaningful to various teams – from front-line customer service to back-office fraud analysts. AI automatically translates complex data patterns into actionable insights, which different departments can understand and act upon.
Furthermore, AI systems can learn how different teams respond to alerts, continuously refining their algorithms to provide more relevant and accurate notifications. A feedback loop is created where the system becomes increasingly effective at identifying which patterns require attention from specific departments. When a potential fraud case emerges, AI can automatically route information to relevant teams while maintaining secure data access controls.
AI and Human Intelligence: The Perfect Fraud-Fighting Partnership
Yet amid this technological revolution, an important truth emerges: AI isn’t the entire solution. The most successful banks have discovered that the magic lies in the synthesis of artificial and human intelligence. While AI excels at pattern detection and initial screening, human analysts provide crucial context and nuanced decision-making that algorithms can’t match.
Building Tomorrow’s Defense
Success in this new era demands a fundamental shift in how banks approach security. Data democracy has become crucial – breaking down departmental silos and creating unified threat intelligence across institutions. Leading banks are updating their AI models weekly rather than quarterly and maintaining flexible defense architectures that can adapt to emerging threats.
For banking leaders, the path forward requires a multi-faceted approach. Success demands investment in scalable AI capabilities, building hybrid teams that combine human insight with artificial intelligence, and active participation in industry-wide threat intelligence sharing.
The question isn’t whether AI can outsmart fraudsters. The question is: can you afford not to find out?
Talk to us today to become a winner in this new era of intelligent security.
]]>Of course, the mental and physical skills of each soldier and thousands of hours of repetitive training that they receive play a role, but also the way the Seals are structured reveals an important aspect of their effectiveness and efficiency.
Navy Seals operate within two structures, a hierarchical command-and-control structure, and an independent web-like structure comprised of small teams at the operation level.
The commanders give out the missions, officers relay them to the troops, and then the Seals carry out their objectives with little micromanagement.
These two structures – a hierarchical tree-like chain of command and a web-like organization on the ground — have combined to give the Seals a reputation of excellence and efficiency.
Organizations can learn a lot from these two types of structures.
A tree structure offers stability. It enforces discipline and ensures orders are conveyed directly and efficiently. However, this structure can only facilitate communication one way at a time: either from commander to soldier or the other way around. It can also slow down the process of communication since any message that must be relayed to the last in the chain of command must pass through every level in the chain.
The web structure, on the other hand, comprises interconnected nodes – every soldier has direct contact with every team member on the ground. Teams have mutual trust and purpose, through shared experiences. As a result, they all understand what the desired outcome is, and what each person needs to do to achieve it quickly. Such teams are highly adaptable and can change course quickly depending on the situation. Webs offer agility and unity, which projects effectiveness and precision.
By combining the tree and web structures within each operation, the Navy Seals have become a well-oiled machine that is the envy of the world.

How Do These Structures Operate?
Traditional organizations have often resembled hierarchical trees. The control of information flow rests with leadership, and the information flows in a unidirectional manner from leadership to employees. Leadership receives feedback from employees in a similar unidirectional manner. Team leads often micromanage tasks, and employees are directed on what to do.
The tree structure was suitable for periods when operational speed was slower, and larger workforces were necessary for scaling. Many organizations care more about efficiency and structure themselves in a way that everyone follows one person’s commands. The problem with this is that one single person alone can’t grasp the complexity that comes with modern problems.
A web structure, on the other hand, can help organizations share information more rapidly among all stakeholders within the organization, from the CEO to the contributors, facilitating adaptive problem-solving and fostering a culture of innovation. By adopting a web-like structure, organizations can enhance their problem-solving capabilities, increase speed, and improve overall resilience. This model empowers employees to contribute to the organization’s success, fostering a sense of ownership and engagement.
Webs present challenges when applied to larger groups. Managing and executing tasks becomes more complex due to the increased number of inputs, potentially slowing down processes. Additionally, web structures demand highly skilled individuals with complementary and equally valued expertise.

Webs Within Trees
Contemporary business challenges necessitate agility and collaboration while remaining aligned with a broader organizational vision. The rise of giants like Amazon, which operates on a both a structured level with its platform services and as an interconnected network of sellers on the platform demonstrates the need for such hybrid structures.
A purely web-based structure may lack the necessary control and accountability in certain areas. A hybrid approach, combining elements of both hierarchical and network structures, may offer the most effective solution. Teams are great at creating cohesiveness, but they also exclude those outside of the team. Smaller teams must make sure they work together with the other teams as a larger team. Multiple teams can share the same overall processes and purpose. Businesses must ensure there is a shared understanding of the context of their work, so they can work towards the organizational vision, and not just that of the team.
The digital age demands a rethinking of organizational structures. While the hierarchical model serves its purpose, the increasing complexity of the business environment necessitates a more fluid and interconnected approach. Embracing a hybrid structure that is robust and agile in adaptation can help organizations position themselves for long-term success as problem solvers.
About the authors:
Ashish Sawant, Head of Sales & Todd Wandtke, Head of Marketing and Customer Success.
]]>